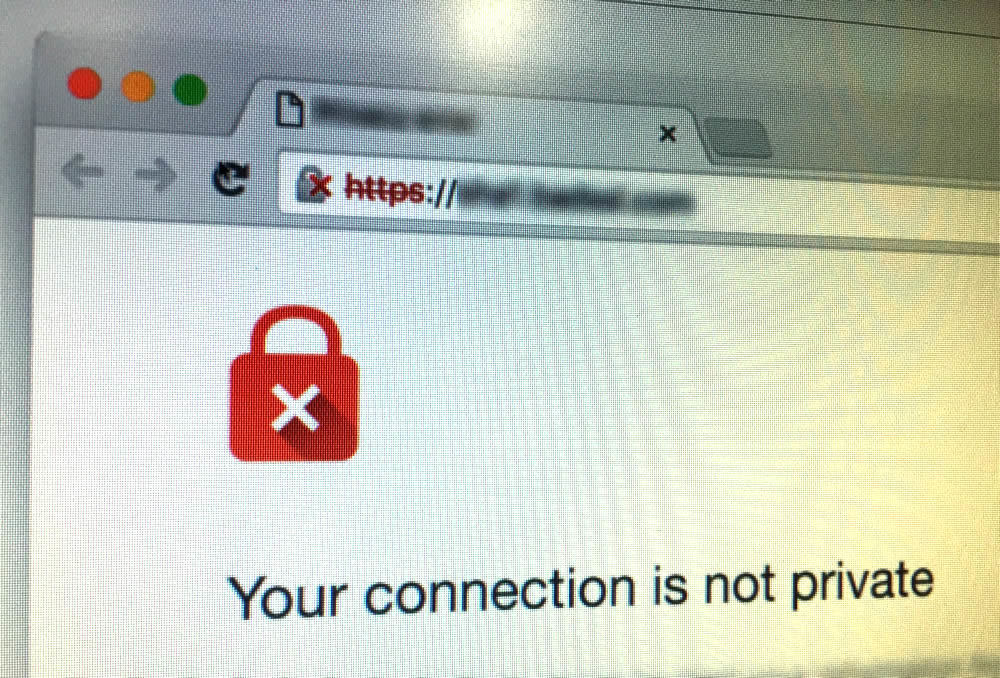
It’s interesting to note that there are still websites without SSL certificates, even though all the search engines have pushed for encryption for years. I would imagine that the issue will become much more critical, at least in the minds of website owners, now that Chrome has started flashing “Not Secure” warnings on unencrypted sites. That’s right – it’s not just the little padlock anymore. Now, your visitors will start seeing a large red warning if you are still operating under HTTP.
As announced, Chrome will mark non-secure pages containing password and credit card input fields as Not Secure in the URL bar.
Why is Google Pushing for Encryption?
Under the radar, a movement has grown that will force all websites to employ encryption. This push for HTTPS to replace the common HTTP or hypertext transfer protocol seems to have taken root. Google announced plans that, in essence, penalize unencrypted websites. Their new policies regarding encryption went into Effect in January 2017.
The Need for Secure Websites
In 2015, U.S. prosecutors charged three men with the cyber-crime of stealing personal information from more than 100 million people. Unsubstantiated claims by Russian hackers stated that they have accessed over one billion usernames and passwords from Internet databases. A global study by the UN found that the chances of being a victim of cybercrime are 12% higher than being subjected to a physical crime.

Google Leads the Crusade for Internet Reform
Based on those sobering statistics, Google began its push for an “encrypted web.” Back in 2014, Google stepped up the campaign against unencrypted websites when, at their I/O Summit, they called for HTTPS to replace the less secure HTTP.
To push the agenda forward, Google first drafted a proposal for the purpose of showing users that their HTTP did not provide data security. Next, they announced that websites with valid HTTPS would rank higher in their search results. In the past, SSL certificates were considered necessary only for websites dealing with banking or e-commerce. Other types of sensitive data, such as medical records, might have been encrypted, but the average blogger or informational site had no need for the certificate.
Google Changed the Structure of the Internet
By increasing the search rank of encrypted sites, Google changed the structure of the internet and the status of unencrypted websites. Since most websites base their viability on that first-page ranking, website owners must follow the new “rule” and obtain their SSL certificate to compete. However, Google is not the only proponent of encryption. Apple and Mozilla both speak strongly for required HTTPS. With these three companies behind the initiative, compliance is not really optional.
As a result, the United States government set a requirement for all .gov websites to be converted to HTTPS by December 2016. While most people would agree that their tax records and social security information needs to be protected, the majority may not feel the same way about local blogs and community bulletin boards. However, the push required ALL internet websites to use HTTPS.
What Does This Mean for Unencrypted Websites?
First, Google displayed a red padlock with an “x” on websites with e-commerce or where visitors logged in that were not already secured through HTTPS. Then, Google began marking ALL non-HTTPS pages collecting sensitive information as “Not Secure.”
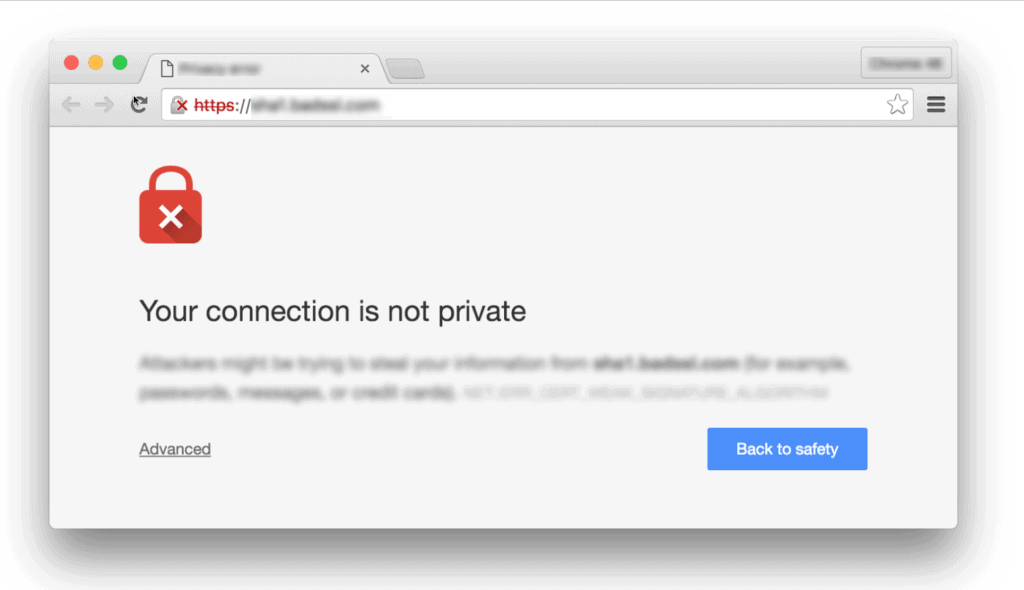
The Pros and Cons of Using SSL
So, what does it matter? Are there drawbacks to switching all websites to HTTPS?
First, let’s take a look at the positive aspects of encryption.
SSL Encrypts Sensitive Information and Protects it From Prying Eyes
As data moves around the internet, it passes from computer to computer on its way to its final destination. Think of it like the old Pony Express system. Information travels from one server to another, where it is sent on the next leg of its journey. During each jump, the potential exists for someone to hijack the transmission. Encrypted data keeps the hijacker from making sense of the information they intercept.
Encryption Provides Authentication and Security for Users
Fraudulent websites litter the internet. The only way someone can be sure they are visiting an authentic website is by checking for their SSL certificate. Google shows trusted sites with a small green padlock next to their URL. Users know that the site has been verified and that they are interacting with a known entity. The visual cue of the green padlock creates a sense of security. Visitors won’t have to dig further to find out whether or not their information is safe.
Secure Transmission is Necessary for PCI Compliance
E-commerce sites that accept credit cards must use an SSL certificate. To comply with audit requirements, they must prove they use encryption of customer financial data. No legitimate e-commerce site can operate without an SSL certificate unless they go through a third party payment processor such as Paypal. In such cases, companies such as Paypal accept responsibility for the handling of customer financial information and hold the required certificates.
The Challenges of Switching from HTTP to HTTPS
The primary reason most websites do not use HTTPS is cost. An SSL certificate can cost upwards of $150 and doesn’t seem necessary for those not handling sensitive information. In 2016, the Internet Security Group, sponsored by Linux, Cisco, Mozilla, and others, began offering TSL (Transport Layer Security) encryption free of charge through participating web hosts. Even though the certificate is free, there may still be some configuration costs. The certificate is not enough. Your web designer needs to code your website, so everything on it loads through HTTPS rather than HTTP. The goal of this project was to eliminate the high costs associated with SSL certificates and further the move to “encrypt the web.
While e-commerce sites will still require a higher level of encryption, these X.509 certificates, being offered at no cost, meet the needs of other sites, not handling data of a sensitive nature.
Overall, the move to encrypt all websites seems to be positive. HTTPS helps protect customers and promote trust. By “forcing” website owners into compliance, Google, and the other internet giants, just might be acting in everyone’s best interests.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding HTTPS
Here are some of the most common questions we receive from our clients.
1. What are SSL and HTTPS?
SSL = Secure Sockets Layer. It’s a digital “certificate” (a big encrypted text file) generated from a trusted SSL provider like Comodo. Anyone can make one. The reason you buy a name brand is that browsers recognize the name brands. A no-SSL certificate will cause a pop-up warning message in a browser for your visitor. This file makes a special connection to a visitor’s browser that encrypts communication.
HTTPS = this is simply the secure version of HTTP – for example, when you are checking out on an e-commerce store, you will almost always see HTTPS in the address bar instead of HTTP.
2. Does this HTTPS requirement apply to me?
In short, Yes. If you require users to log in or you accept payments on your website, then it is an absolute must. But, even if you don’t, HTTPS will factor into rank results. In order to compete, you will need to be secure.
3. Why should I invest in SSL?
There are a couple of reasons why your website should be entirely covered by HTTPS:
- Google has confirmed that they now give additional ranking benefits to websites that are using HTTPS:// on every page.
- People tend to perceive sites with HTTPS as “safe” and “trusted.” With cyber security becoming an increasingly relevant issue, this trust is important.
HTTPS will build credibility with both the search engines and your visitors. It’s a win-win situation.
4. How much does it cost?
This is, of course, the big question for most companies. The beautiful thing is that for many, the certificate costs nothing. For websites accepting online payments, you will need a different type of SSL Certificate, but you can receive a discount through Effect if you purchase one that is valid for several years. Certificates do need to be installed and renewed. There may be minimal costs associated with the setup.
Let Us Help You Succeed!
We can meet your SEO needs and help you rank higher in the Local Pack, organic search, and YouTube. Whatever your business goals, we will work to build an SEO strategy that reaches them. We do everything we can to work with our clients to make web design and online marketing affordable. Contact us for more information.